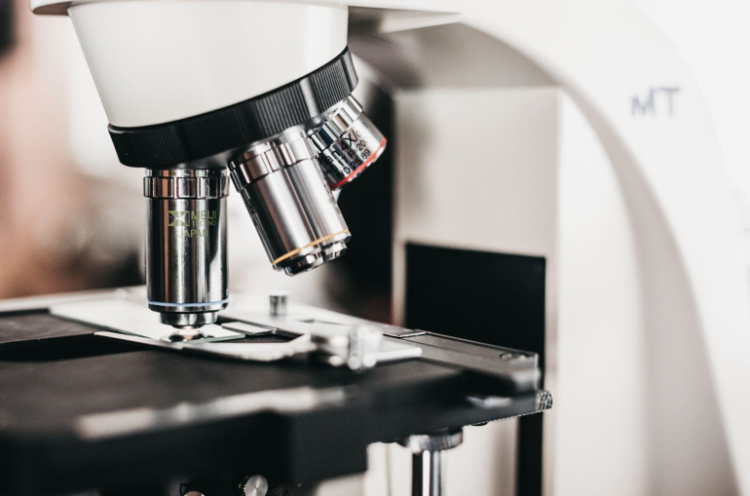
Histology involves studying cells and tissues under a microscope. This process forms an integral part of biology, medicine and veterinary science as well as several sub-disciplines within these fields.
Histopathologists are highly sought after by pharmaceutical and medical technology companies to test their products on laboratory animals, and also assist in autopsies and forensic investigations to help address unexplained deaths.
Table of Contents
What is Histology?
Histology is the scientific study of biological tissue structure by observing thin sections under microscopes.
It’s an essential tool in biology, medicine and veterinary science; specifically hematoxylin and eosin are two histology stains commonly used to color various cell and tissue types to help those examining under a microscope distinguish them.
Examples include pale red tissue fluid coloration for cytoplasm (tissue fluid), red muscle coloring for muscle, blue cartilage coloration for cartilage and deep blue coloration for bones.
Pathologists specialize in histology to detect any indications of disease in tissue samples taken from an organic body during procedures or operations such as colonoscopies or breast biopsies. You can click the link for a histology guide that can help explain this process further. Histologists may suggest having biopsies performed if they suspect lumps or moles, or use histology to analyze any tissue taken as part of these processes.
Histopathology can be used to diagnose cancers and other diseases of the blood vessels, digestive tract, respiratory system and reproductive organs. Autopsies and forensic investigations often employ histopathology as part of their investigations into unexplained deaths.
Histology involves fixing tissue with chemicals such as formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde to preserve it and then cutting thin sections which are stained and examined under the microscope.
Histopathology may also include immunohistochemistry (identifying proteins) and chromosomal studies (which genes may be affected). You can visit this helpful site for more information on chromosomal studies. Therefore it’s essential that any test results be discussed with your physician so they can explain what this report means for you personally.
Staining
Staining is an increasingly popular technique in histology to reveal microscopic details of cells and tissues. This technique uses dyes which bind with specific molecules found within tissue samples to reveal microscopic details. Furthermore, different staining methods target different structures or areas within samples.
Ziehl-Neelsen and Gomori methenamine silver are considered vital stains, while those which mark acid-fast organisms (Ziehl-Neelsen) or fungal walls (Gomori methenamine silver) are classified as non-vital stains.
Preparation
Histology involves microscopic examination of tissue samples to help diagnose issues and recommend treatment solutions. Histology requires multiple steps for turning raw samples into high quality slides that are ready for microscopic analysis.
Tissue fixation, which prevents samples from degrading upon death due to natural enzymes, is the initial step. Samples typically remain immersed for 24-48 hours in neutral buffered formalin solution for this step.
Once biopsies are fixed, most are stained with hematoxylin and eosin, making the proteins visible while nuclei appear dark blue/purple.
Other stains may highlight specific structures within tissue; Malloy’s Trichrome stain colors cytoplasm pale red; muscle orange; cartilage purple; and bone deep blue.
After embedding tissues in paraffin wax, slices are cut using a microtome and slides are produced.
Visualization
Virtual Reality (VR) offers immersive ways of exploring scientific data. Scientists can examine and interact with images at high resolution and scale, helping them better comprehend tissue or organ structures.
VR technology offers clinicians and students an immersive way of exploring complex 3D anatomy. Unfortunately, its widespread adoption for histology visualization remains limited.
VR can also be used for many forms of histological analysis including 3D modeling and visualization of serial sections.
Interpretation
Your doctor may suggest performing a biopsy and histology examination of any suspicious moles, lumps or areas of tissue you may have. This medical procedure entails taking a small tissue sample from the area in question for examination under a microscope.
Histology laboratories specialize in processing and staining samples to make them more visible under a microscope, offering applications in medical diagnosis, scientific research, autopsy as well as forensic science investigations. You can click the link: https://medicine.yale.edu/pathology/clinical/autopsy/reasons/ to learn more about the information professionals can obtain from an autopsy.
Pathologists, or medical doctors trained in histopathology, perform histopathology examinations on specimens collected from either patients or autopsies or forensic investigations.
Their examination involves dissecting tissue into sections for microscopic study under a microscope, with results potentially impactful in terms of treatment options and prognosis; additionally it allows manufacturers of pharmaceuticals and chemicals to understand how their products will react when exposed to human tissue in order to avoid unintended side effects or unnecessary risks.