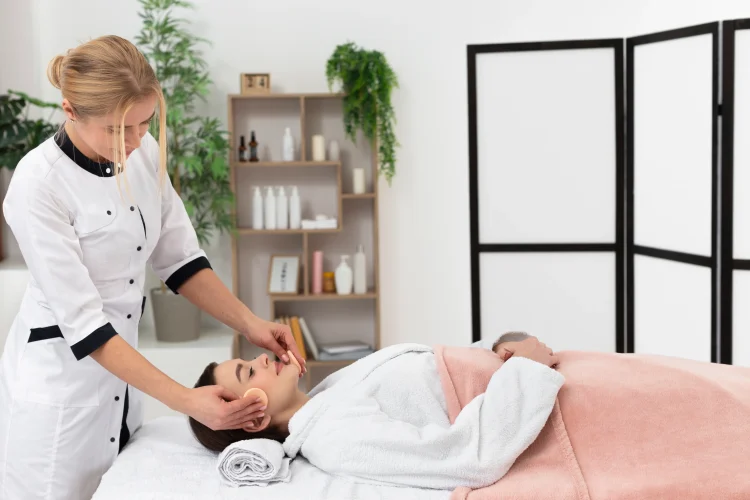
The most effective treatments for melasma go beyond simple pigment reduction, focusing instead on altering the skin’s memory. Melasma is more than a surface blemish; it is a complex pattern imprinted by hormonal changes, UV exposure, and genetic factors. It appears as symmetrical, patchy discolorations that resist easy solutions. Its persistent and recurring nature requires a comprehensive approach rather than a single method. Successful treatment involves rebalancing the skin’s system and effectively managing melanocytes for clear skin.
We partnered with one the best Med Spas in Los Angeles to ensure a clinically correct treatment guide. Beverly Wilshire Aesthetics Beverly Hills was incredibly knowledgeable and such a useful resource.
Table of Contents
1. Hydroquinone Cream (2-4%): The Gold Standard Inhibitor
What It Is
Hydroquinone is widely recognized as a primary treatment for melasma. This powerful compound is the leading choice for topical depigmentation, known for its ability to directly address melanin production.
How It Works
Hydroquinone works by blocking tyrosinase, a crucial enzyme in melanin production. By halting this step, hydroquinone reduces the overproduction of melanin, gradually lightening affected areas.
Results + Benefits
Visible reduction in pigmentation can be seen within 4-6 weeks, with optimal clarity around 8-12 weeks. Its precise action corrects discoloration, resulting in a more even complexion.
Treatment Experience
Application involves a thin layer directly on hyperpigmented areas to avoid unwanted lightening of surrounding skin. Treatment starts every other night, increasing as tolerated.
Recovery + Aftercare
To prevent rare side effects like ochronosis, a cycling approach is recommended: 3-4 months of use followed by a one-month break. Daily use of SPF 50+ sunscreen is crucial to protect results.
2. Tretinoin (Retinoic Acid): The Cellular Accelerator
What It Is
Tretinoin, a derivative of vitamin A, is essential in melasma treatment, promoting cell turnover and pigment normalization.
How It Works
Tretinoin accelerates skin cell renewal, shedding pigmented cells and dispersing melanin, leading to a more even skin tone.
Results + Benefits
Improvements in skin texture and pigmentation appear within 8-12 weeks, with significant results after six months of consistent use.
Treatment Experience
Treatment begins with a low concentration, applied 2-3 nights weekly, gradually increasing as skin adjusts.
Recovery + Aftercare
Application should be on dry skin to reduce sensitivity, with a ceramide-rich moisturizer enhancing the skin barrier. Daily SPF 50+ sunscreen is necessary to protect the renewed skin.
3. Combination Therapy (Triple Therapy/Kligman’s Formula): The Synergistic Approach
What It Is
For resistant melasma, combination therapy using Kligman’s Formula targets pigmentation on multiple fronts.
How It Works
This formula combines hydroquinone, tretinoin, and a corticosteroid to enhance penetration, turnover pigmented cells, and reduce irritation.
Results + Benefits
This approach offers accelerated pigment reduction, especially for moderate-to-severe melasma.
Treatment Experience
Evening application is gradual to ensure skin adapts. The corticosteroid is limited to prevent side effects.
Recovery + Aftercare
Maintenance without the steroid follows the intensive phase, with strict sun protection to prevent recurrence.
4. Chemical Peels (Glycolic Acid, Salicylic Acid, TCA)
What It Is
Chemical peels offer a controlled method to manage melasma by resurfacing the skin.
How It Works
Acid solutions dissolve bonds of damaged cells, promoting turnover and revealing less pigmented skin.
Results + Benefits
A series of treatments provides significant pigment reduction and skin texture improvement.
Treatment Experience
Pre-treatment priming optimizes outcomes, with sessions spaced to allow skin regeneration.
Recovery + Aftercare
Post-treatment, the skin is vulnerable to UV light, necessitating strict SPF 50+ use.
5. Laser and Light Therapies (Q-Switched, Fractional, IPL)
What It Is
When topical treatments are insufficient, laser and light therapies offer advanced management of melasma.
How It Works
Lasers use light to break down melanin deposits, which the body then clears naturally.
Results + Benefits
Multiple sessions result in significant pigment reduction and improved skin quality.
Treatment Experience
Pre-treatment priming and careful settings minimize inflammation, with sessions spaced appropriately.
Recovery + Aftercare
Sun avoidance and daily SPF 50+ application are critical post-treatment.
6. Vitamin C Serums (L-Ascorbic Acid): The Antioxidant Option
What It Is
Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant and mild inhibitor of pigment production, essential in melasma protocols.
How It Works
It neutralizes UV-induced free radicals and suppresses pigment production, enhancing skin brightness.
Results + Benefits
Daily use improves brightness and reduces pigmentation, strengthening skin defenses.
Treatment Experience
Morning application of a stable serum creates a protective antioxidant layer.
Recovery + Aftercare
Follow with SPF 50+ to enhance photoprotection, storing the serum properly to maintain potency.
7. Kojic Acid and Arbutin Serums: Gentle Correctors
What It Is
Kojic acid and arbutin offer natural, mild alternatives for pigment correction.
How It Works
These inhibitors block tyrosinase, reducing melanin production for sensitive skin.
Results + Benefits
Gradual lightening over 12+ weeks, well-suited for long-term use.
Treatment Experience
Twice-daily application ensures maximum absorption and effectiveness.
Recovery + Aftercare
Paired with Vitamin C for enhanced protection and pigment correction.
8. Sunscreen and Sun Avoidance (SPF 50+, Broad Spectrum): The Foundation
What It Is
Sun protection is critical in managing melasma and preserving treatment results.
How It Works
Broad-spectrum sunscreens block UV triggers, preventing melanin overproduction.
Results + Benefits
Prevents worsening of melasma and maintains treatment outcomes.
Treatment Experience
Daily application of SPF 50+ is mandatory, with reapplication during exposure.
Recovery + Aftercare
Includes additional sun protection measures like hats and shade-seeking.
9. Microdermabrasion and Dermaplane: Supporting Exfoliation
What It Is
These methods support melasma management by exfoliating outer skin layers.
How It Works
They remove dead cells, enhancing topical treatment penetration.
Results + Benefits
Provide immediate brightening and smoother skin texture.
Treatment Experience
Strategically scheduled to complement core therapies.
Recovery + Aftercare
Ensures SPF 50+ application post-procedure.
10. Oral Medications (Tranexamic Acid): A Systemic Approach
What It Is
Oral tranexamic acid targets melasma systemically, addressing internal pathways.
How It Works
Inhibits plasmin, reducing melanocyte activity and providing comprehensive depigmentation.
Results + Benefits
Significant improvement in stubborn melasma with long-lasting results.
Treatment Experience
Prescribed under medical supervision, often alongside topical treatments.
Recovery + Aftercare
External protection with sunscreen is still essential.
Conclusion
Melasma requires a thoughtful approach, combining various treatments tailored to individual needs. Effective management involves a blend of topical agents, systemic approaches, and consistent sun protection to achieve and maintain clear, radiant skin